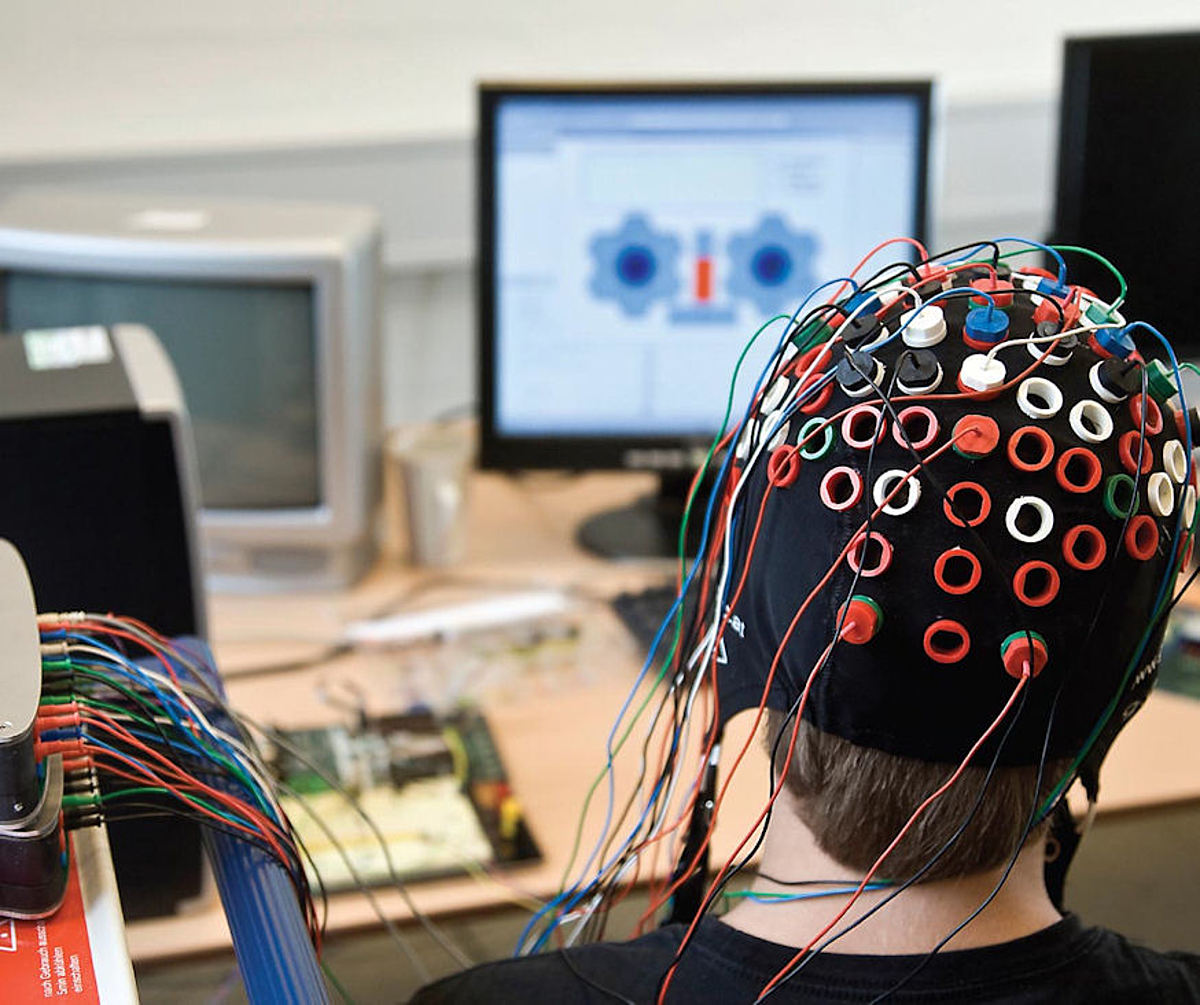
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are at the forefront of neurotechnology innovation, heralding a new era in how humans interact with machines. These cutting-edge devices, such as brain chip implants developed by companies like Neuralink, have the potential to transform lives by allowing individuals to control computers, prosthetics, and even communicate through thought alone. As researchers and entrepreneurs explore various BCI applications, the market is poised for explosive growth, potentially reaching $400 billion in the U.S. alone. However, alongside the remarkable benefits lies a complex web of ethical challenges, including neurotechnology risks and the haunting specter of mind control ethics. The rapid advancement of BCIs invites not only excitement but also urgent discussions about consent and the potential misuse of such powerful technology.
Cognitive interface technologies, often referred to as brain-machine interfaces, are rapidly advancing, offering unprecedented potential for bridging human cognition with digital systems. By enabling direct communication between the brain and computers, these devices can significantly improve the quality of life for those with mobility impairments or neurological disorders. The implications of such technology extend beyond therapeutic applications, raising important discussions around the ethical dimensions of mind control and mental privacy. As the field grows, it is crucial to stay vigilant about the neurotechnology risks involved, particularly concerning the historical lessons of psychological manipulation. Consequently, the dialogue surrounding these innovations must balance their transformative benefits with the need for responsible governance.
The Promise of Brain-Computer Interfaces in Medical Advances
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a revolutionary leap in neurotechnology, harnessing the power of the brain to facilitate interaction with computers and external devices. The potential applications are vast: from enabling individuals with mobility impairments to operate prosthetic limbs to aiding those with speech difficulties in communicating more effectively. As seen in the groundbreaking case of Noland Arbaugh, the ability to control a computer mouse using thought alone highlights how BCIs can transform the lives of individuals suffering from disabilities. This innovation not only improves quality of life but also opens doors to a wider range of practical applications as the technology matures.
With estimates suggesting that the BCI market could reach about $400 billion in the U.S., there is significant interest in advancing this technology further. Researchers and companies are working collaboratively to refine brain chip implants, aiming to unlock new possibilities in treating various neurological conditions. However, the journey is not solely about technological advancements; it also involves understanding the integration of ethical standards to ensure the responsible use of this technology. As we venture into this promising territory, it becomes essential to analyze not just the benefits but also the ramifications of BCI applications on human autonomy and consent.
Neuralink Technology: Benefits and Ethical Considerations
Neuralink, a pioneer in the BCI field, aims to develop advanced brain chip implants that can transform the interface between humans and machines. By embedding these chips into the brain, individuals may achieve unprecedented control over technology using only their thoughts. This could significantly enhance the treatment of neurological disorders, improve cognitive functions, and even facilitate direct communication through thought. As the technology evolves, there is hope that it will not only restore lost functions but also expand human capabilities beyond current limitations, offering new solutions for various medical conditions.
However, the rise of Neuralink technology raises critical ethical questions surrounding the implications of brain chip implants. As highlighted in discussions about mind control ethics, there are concerns regarding the potential misuse of such advancements. If BCIs can decode and influence thoughts, the risk of infringing on personal autonomy and mental privacy becomes inevitable. The past experiences with unethical experiments during the Cold War serve as a stark reminder of how the pursuit of mind control can slip into the hands of those with ulterior motives. As we pursue these innovations, it is vital to establish robust ethical frameworks to safeguard individuals’ rights and ensure that these technologies serve humanity’s best interests.
Neurotechnology Risks: Analyzing Historical Precedents
While the advancements in neurotechnology present immense potential, it is critical to reflect on historical precedents to understand their implications fully. The experiences of the Cold War era, where agencies like the CIA attempted psychological manipulation through unethical experiments, showcase the hazards of unregulated technology. Projects such as MKUltra were aimed at controlling behavior and information extraction, resulting in considerable harm to individuals involved. As brain-computer interfaces advance, the specter of these historical abuses raises alarms about the possible consequences of tampering with human cognition.
The lessons from the past should inform our approach to modern BCI technologies. The same spirit of inquiry that drives innovation must coexist with vigilance and ethical oversight. Meier’s report emphasizes that while contemporary BCIs may avoid the severe repercussions seen in earlier psychological operations, they are still fraught with risks to individual consent and self-determination. As the technology becomes more sophisticated, the possibility of unintended behavioral changes, as observed in certain deep brain stimulation cases, underscores the necessity of prioritizing ethical standards to prevent repeating the mistakes of history.
Mind Control Ethics: The Need for Strong Regulation
As brain-computer interfaces become more integrated into medical applications, discussions regarding mind control ethics have become increasingly relevant. The capacity for BCIs to alter thoughts and behaviors introduces potential for significant ethical dilemmas. The capability to decode brain signals can blur the line between therapeutic use and exploitation. If the technology can manipulate thoughts, how do we ensure that it is used responsibly? The urgency for establishing robust regulatory frameworks that protect individual rights while fostering innovation cannot be overstated.
Many researchers and ethicists argue that proactive measures should be enacted to delineate acceptable boundaries for BCI applications. Articulating what constitutes informed consent in the context of neurotechnology is paramount; individuals must fully understands the potential implications of their decisions regarding brain chip implants. Additionally, balancing technological advancement with ethical accountability can encourage a more conscientious approach to developing this transformative technology. As we advance in this field, we must prioritize ethical considerations to prevent the potential fallout of mind control exerting undue influence over human behavior.
The Future of Brain-Computer Interfaces in Society
The future of brain-computer interfaces promises a radical transformation in how society interacts with technology. As BCI technology matures, its applications could extend to various domains such as education, communication, and even entertainment. Imagine students using BCIs to enhance learning by directly accessing information or individuals enjoying video games through thought alone. The integration of such technology into daily life could herald a new era of human enhancement and connectivity, bridging gaps that were once insurmountable for many.
However, as we envision these advances, it is crucial to consider how society will adapt to the widespread adoption of BCIs. Issues of accessibility, equity, and inclusion must be addressed to ensure that the benefits of neurotechnology do not disproportionately favor certain socioeconomic groups. Furthermore, as with any revolutionary technology, there will be resistance and apprehension concerning privacy, security, and the potential for misuse. Thus, a comprehensive societal dialogue must precede the deployment of brain-computer interfaces to navigate the complexities of this new frontier responsibly.
Public Perception of Neurotechnology: Challenges and Opportunities
Public perception of neurotechnology, particularly regarding items like brain chip implants, plays a pivotal role in determining the trajectory of their acceptance and implementation. While there is excitement surrounding the potential of BCIs to change lives, there is also a significant amount of skepticism rooted in fears about privacy, autonomy, and even exploitation. To harness the potential benefits of these technologies, it is crucial to engage with the public through education and transparent discussions about how they work, their intended use, and the safeguards against misuse.
To foster an informed public discourse, stakeholders, including scientists, ethicists, and technology companies, must prioritize community engagement. By addressing concerns head-on and highlighting the regulatory measures in place to prevent abuse, a more balanced understanding can emerge. This openness not only alleviates fears but also creates opportunities for collaborative advancements amongst various sectors of society. Educating the public about the safety, efficacy, and ethical implications of BCI technologies will be foundational as we move toward a future intertwined with these groundbreaking tools.
Global Perspectives on BCI Development
The global landscape for brain-computer interface development is diverse, with various countries advancing their own neurotechnology initiatives at different speeds. Nations like the United States lead in terms of investment and research, primarily driven by companies like Neuralink. However, other countries are also making significant strides, particularly in Asia, where governments execute strategic plans to foster neurotechnology research in health and education. This worldwide interest showcases both a competitive race within the tech industry and a commitment to harness the power of BCIs to improve human capabilities.
Yet, this growth also brings to light the varying regulatory frameworks governing BCI technologies across different regions. As some nations may prioritize innovation, others might emphasize stringent ethical standards to protect citizens from potential abuses. This disparity can lead to challenges related to international collaboration, fostering a need for universal standards in the development and application of brain-computer interfaces. As stakeholders navigate the global landscape of BCIs, championing ethical considerations alongside technological advancements will be essential to achieving a balanced and responsible approach.
The Intersection of Neurotechnology and Privacy
As brain-computer interfaces increasingly enter the realm of daily life, the intersection of neurotechnology and privacy raises significant concerns. With BCIs capable of capturing analysis of brainwave patterns, there exists an inherent risk to individual mental privacy and the potential for unauthorized access to thoughts. As these devices gain traction, it becomes imperative to explore how to protect users from potential invasions of their private mental space. The challenge lies in ensuring that individuals retain control over their neurological data and that it is not exploited for malicious purposes.
Developing clear guidelines and regulations surrounding privacy in the context of neurotechnologies is vital. This includes creating frameworks dictating how data gathered from brain-computer interfaces can be stored, shared, and used. By establishing strong privacy protections, the public can feel more secure in the use of BCIs, ultimately leading to greater acceptance and integration of this technology into society. Innovative solutions, such as encrypted neuro-data storage and user-controlled access procedures, can help safeguard against potential breaches, ushering in an age of responsible and ethical BCI usage.
The Role of Education in Advancing BCI Technologies
Education plays a critical role in fostering understanding and acceptance of brain-computer interface technologies. By integrating neurotechnology topics into academic curricula, schools can cultivate interest among students in fields such as neuroscience, engineering, and ethics. Educators have a unique opportunity to shape the next generation of innovators and researchers, equipping them with both technical skills and a strong ethical framework to navigate the complex landscape of neurotechnology. This proactive approach ensures that young minds are prepared to tackle the challenges and opportunities presented by BCIs.
Moreover, fostering public awareness through educational outreach initiatives can demystify BCIs and promote informed discussions about their potential. Workshops, seminars, and community forums could be pivotal in addressing concerns surrounding neurotechnology, emphasizing its benefits while thoughtfully engaging with ethical considerations. By encouraging a knowledgeable society, we create a collective vigilance that holds stakeholders accountable and promotes responsible advancements in the realm of brain-computer interfaces. Education, therefore, emerges as a pivotal pillar in both the development and societal integration of BCI technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) and how do they work?
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are advanced neurotechnology systems that facilitate direct communication between the human brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetic limbs. By interpreting electrical signals from the brain, these interfaces enable individuals to control devices using their thoughts, offering significant potential for those with disabilities.
What role does Neuralink technology play in brain-computer interfaces?
Neuralink technology, developed by Elon Musk’s company, is a pioneering example of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). It focuses on implanting brain chips that can decode neural signals, allowing users to perform tasks such as controlling a computer mouse or communicating their thoughts, which could revolutionize treatments for neurological conditions.
What are the current applications of BCIs in medicine?
Current BCI applications in medicine include assisting individuals with paralysis to control prosthetic limbs, enabling speech for those who can’t communicate verbally, and providing rehabilitation support for stroke victims. These applications demonstrate the transformative potential of brain-computer interfaces for improving quality of life.
What risks are associated with brain chip implants and BCI technology?
Brain chip implants and BCI technology come with neurotechnology risks, including the potential for privacy violations, mental health impacts, and behavioral changes caused by unintended stimulation. These risks necessitate careful ethical considerations and robust regulations to ensure user safety and consent.
How does the ethics of mind control relate to brain-computer interfaces?
The ethics of mind control and brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) are intertwined, as advancements in BCI technology raise concerns about mental privacy and the potential for behavioral manipulation. Discussions around mind control ethics emphasize the importance of safeguarding consent and self-determination in the face of evolving neurotechnology.
Could brain-computer interfaces enable mind control in the future?
While brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have the potential to decode thoughts and influence behavior, the idea of mind control raises significant ethical implications. Researchers caution that, without ethical oversight, the technology could be misused for coercive purposes, paralleling historical misuse in psychological manipulation.
What can we learn from the historical context of mind control experiments regarding BCIs?
Examining past mind control experiments, particularly during the Cold War, offers valuable lessons for the development of brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). These historical precedents highlight the potential dangers of psychological manipulation and the need for stringent ethical guidelines to prevent misuse of neurotechnology.
What is the market potential for brain-computer interfaces?
The market potential for brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) is substantial, with estimates suggesting it could reach around $400 billion in the U.S. alone. This growth is driven by increasing demand for innovative therapeutic solutions for spinal cord injuries, strokes, and related conditions.
How might BCIs transform the lives of individuals with disabilities?
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) have the potential to dramatically transform the lives of individuals with disabilities by enabling them to control devices with their thoughts. This technology can facilitate independence, improve communication, and enhance mobility for those suffering from conditions like paralysis or neurological disorders.
What are the future directions of research in brain-computer interface technology?
Future research in brain-computer interface (BCI) technology aims to enhance the accuracy and usability of brain chip implants, explore new therapeutic applications, and address ethical concerns regarding privacy and consent. Innovations could lead to more effective treatments for various neurological conditions and improved user experiences.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) | Assistive devices that allow direct communication between the brain and external devices, such as computers or prosthetics. |
| Recent Advancement | Noland Arbaugh was the first recipient of a brain chip implant from Neuralink, enabling him to control digital devices with his thoughts. |
| Market Potential | The potential market for BCIs in the U.S. is estimated at around $400 billion. |
| Historical Concerns | Past experiments, such as MKUltra, raise ethical concerns regarding psychological manipulation and mind control. |
| Ethical Implications | The development of BCIs may lead to breaches of mental privacy and consent. |
| Global Competition | Advancement in BCI technology is seen as crucial for maintaining a competitive edge against global adversaries. |
Summary
Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) represent a groundbreaking leap in neurotechnology, offering immense potential to enhance the lives of individuals with disabilities. However, as this technology advances, it simultaneously brings forth ethical dilemmas that echo historical abuses, particularly in areas concerning mental autonomy and consent. Caution must be exercised in the development and implementation of BCIs to prevent potential misuse that could infringe on personal freedoms and rights. As we forge ahead, society must balance innovation with moral responsibility to ensure that brain-computer interfaces serve as tools for empowerment rather than control.