MicroRNA research has revolutionized our understanding of gene regulation, especially following the groundbreaking discoveries by Nobel laureate Gary Ruvkun. His work with C. elegans, a model organism, unveiled the intricate mechanisms by which tiny RNA molecules control gene expression, fundamentally altering our approach to genetics. This fascinating field of study has not only paved the way for novel RNA therapies targeting critical health issues such as heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer’s but has also opened doors to numerous advancements in the biomedical sector. With more than 1,000 microRNAs identified in the human genome, the potential applications are vast, raising significant interest from scientists and pharmaceutical companies alike. Ruvkun’s pioneering contributions were critical in establishing microRNAs as essential players in biology, destined for recognition through the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology, marking a long journey from obscurity to accolade in the scientific community.
The exploration of small non-coding RNAs, particularly microRNA, represents a pivotal era in genetic research that has captured the attention of many within the scientific community. These minute regulatory molecules, originally studied in the model organism Caenorhabditis elegans, have shown profound implications not only for gene expression control but also for the development of innovative therapeutic approaches in medicine. As researchers have uncovered their significant roles in various biological processes, the push towards utilizing RNA-based therapies has gained momentum, promising hope for conditions such as chronic illnesses and neurodegenerative disorders. The ongoing investigation into the intricacies of microRNA interactions underlines its critical position at the frontier of genetic science, fostering a collaborative atmosphere among biologists, clinicians, and researchers. As awareness and funding continue to build, the field stands poised for transformative breakthroughs that could reshape our understanding of genetics and health.
The Groundbreaking Discovery of microRNA
In 1992, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros made a revolutionary discovery in molecular biology — the existence of microRNA (miRNA), which would dramatically change our understanding of gene regulation. This monumental finding, documented in their 1993 publication in the prestigious journal Cell, unveiled how small RNA molecules play a pivotal role in the control of gene expression. Despite the initial skepticism from the broader evolutionary biology community, which did not immediately recognize the implications of their work, the discovery marked the inception of a new field of research that adds significant depth to our understanding of genetic processes across various organisms, including the influential model organism, C. elegans, which they utilized in their studies.
Ruvkun’s initial struggle for recognition speaks volumes about the nature of scientific progress, often requiring years — even decades — for a discovery to reach its full potential in the scientific community. The groundwork laid by Ruvkun and Ambros has now blossomed into a robust field of study that not only includes a deeper understanding of miRNA but has also sparked interest in potential medical applications. Today, microRNA research reveals that these tiny RNA molecules are intrinsic to developmental biology and clinical applications, hinting at their profound impact on evolutionary mechanisms and therapeutic avenues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did Gary Ruvkun play in the discovery of microRNA and gene regulation?
Gary Ruvkun was pivotal in the groundbreaking discovery of microRNA in the early 1990s, which unveiled a new dimension of gene regulation in the C. elegans roundworm. His research, along with colleague Victor Ambros, laid the foundation for understanding how microRNAs influence gene expression and protein production, earning them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 2024.
How do microRNAs contribute to gene regulation in humans?
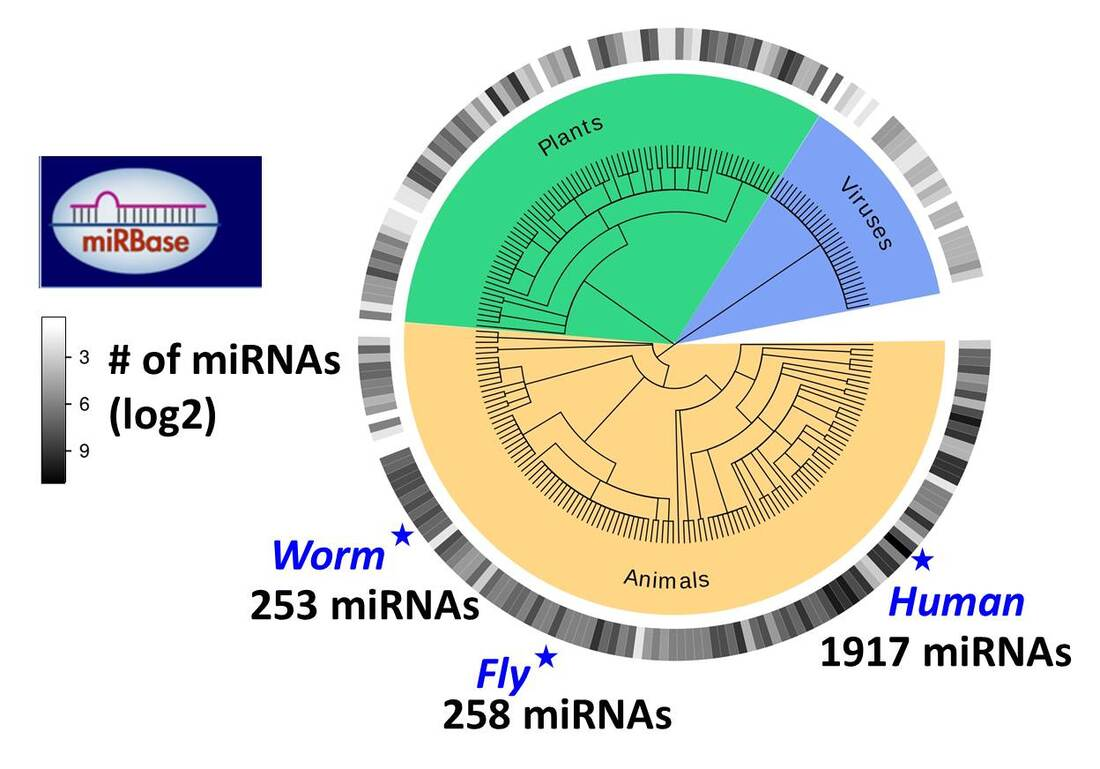
MicroRNAs play a critical role in gene regulation across various species, including humans. They are small RNA molecules that can inhibit gene expression, thereby controlling the production of proteins. Studies show that the human genome contains around 1,000 microRNAs, which are essential for the regulation of most human protein-producing genes, making microRNA research a vital area in genetics.
What diseases are being targeted by RNA therapies involving microRNA research?
RNA therapies that leverage microRNA research are currently in clinical trials to treat several diseases, including heart disease, cancer, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. This innovative approach harnesses the regulatory power of microRNAs to potentially improve patient outcomes by regulating the expression of disease-related genes.
Why is the study of microRNA in organisms like C. elegans important for broader biological research?
The study of microRNA in model organisms like C. elegans is crucial because it provides insights into the fundamental mechanisms of gene regulation that are conserved across species. Discoveries made in C. elegans have implications for understanding similar processes in higher organisms, including humans, thereby enhancing our overall knowledge of genetics and potential therapeutic targets.
How has federal funding influenced microRNA research and its applications?
Federal funding has significantly shaped the landscape of microRNA research, enabling scientists like Gary Ruvkun to explore gene regulation without financial constraints. The support from organizations such as the NIH has allowed groundbreaking discoveries, leading to the development of RNA-based therapies and the growth of biotechnology companies focused on genetic diseases.
What advancements have been achieved in RNA therapies as a result of microRNA research?
Advancements in RNA therapies stemming from microRNA research have led to innovative treatments for multiple diseases. Researchers have developed therapies that utilize the unique properties of microRNAs to regulate gene expression, demonstrating promising results in clinical trials for conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
How do microRNAs impact the development of new biotechnology companies?
The exploration of microRNAs has catalyzed the formation of new biotechnology companies focused on RNA therapeutics. Companies like Alnylam Pharmaceuticals have emerged from this research, leading to significant advancements in treating genetic disorders, showcasing how microRNA research fosters innovation and economic growth in the biotech sector.
What are the future prospects for microRNA research in the field of gene therapy?
The future prospects for microRNA research in gene therapy are bright, with ongoing exploration of microRNAs’ potential to fine-tune gene expression. As technology advances, researchers anticipate developing more targeted therapies that leverage microRNA’s regulatory capabilities, paving the way for innovative treatments for various genetic disorders.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, earning the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
| Initially, the discovery of microRNA did not receive widespread recognition in the evolutionary biology community. |
| The research was primarily funded by NIH and targeted a niche community interested in RNA and model organisms like C. elegans. |
| MicroRNAs play essential roles in gene regulation, with approximately 1,000 identified in the human genome controlling protein production. |
| Clinical trials are underway for therapies targeting microRNAs for diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. |
| Federal funding has been critical to the success and longevity of Ruvkun’s research and the field of microRNA. |
| The growth in interest and research in the microRNA field has led to significant advancements and commercial opportunities. |
Summary
MicroRNA research has gained substantial momentum since its initial discovery in the early 1990s, culminating in a Nobel Prize for its pioneers, Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros. Their groundbreaking work revealed the crucial role of microRNAs in gene regulation, which has paved the way for innovative therapies targeting various diseases. As research continues to evolve and expand, the significance of microRNA in understanding genetics and developing treatments is becoming increasingly apparent, highlighting the necessity of sustained investment in this vital area of science.